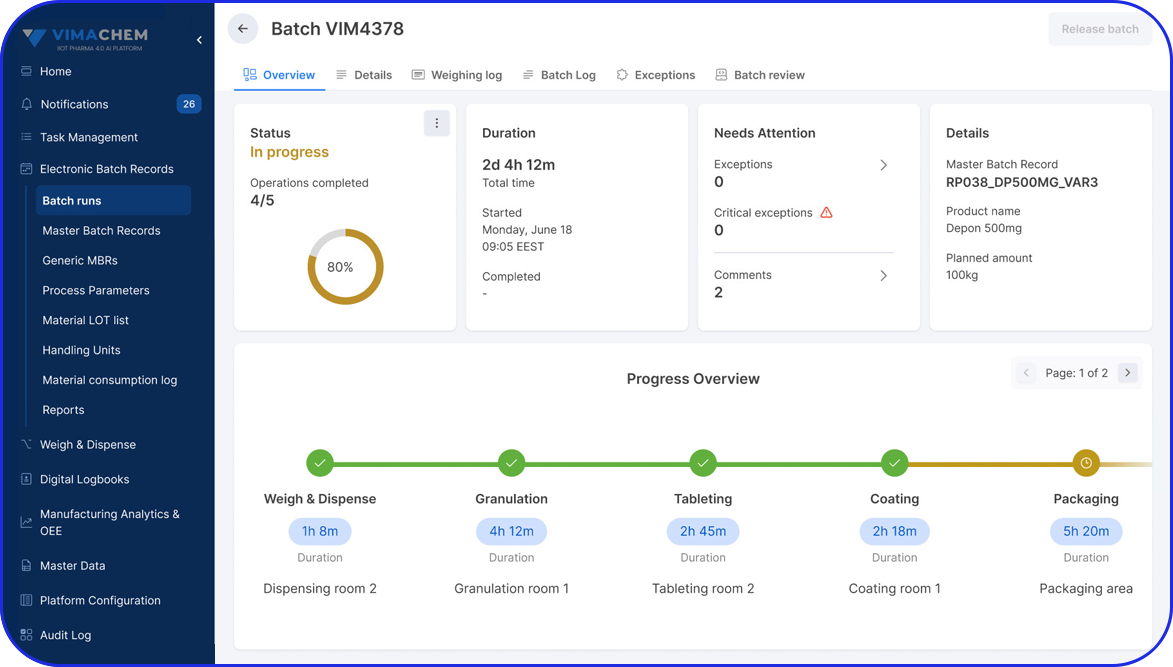
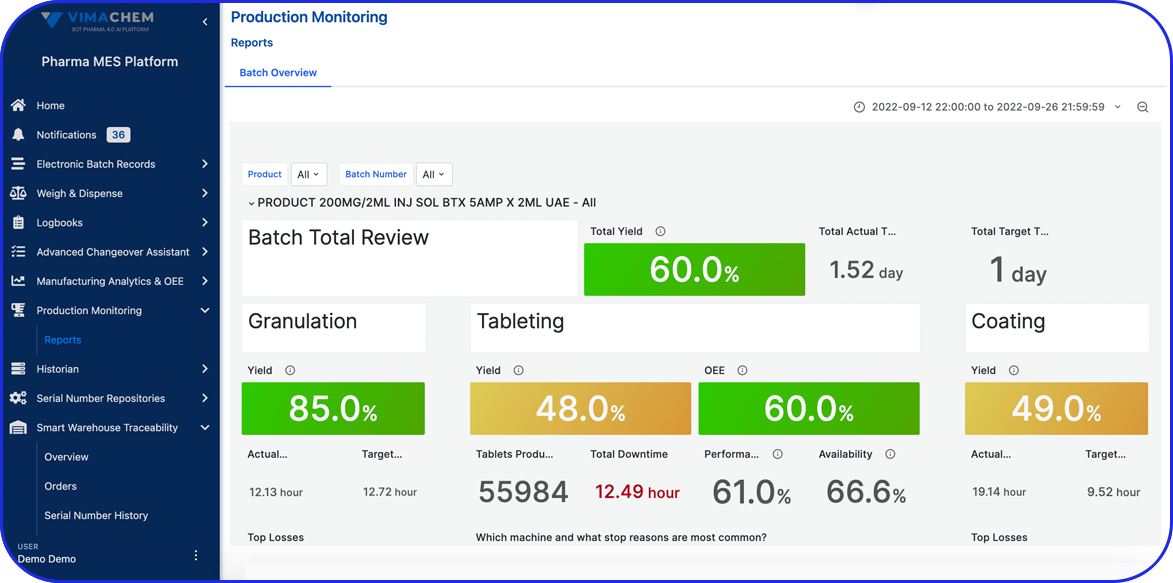
What's a Master Batch Record & its Role in the Pharma Industry
Are you navigating the complexities of pharmaceutical manufacturing?
If so, you’ll need a roadmap – a master blueprint that guides you through every step and ensures precision and compliance.
That’s the essence of a Master Batch Record (MBR) – your fundamental protocol for transforming raw materials into life-saving medications.
What is a Master Batch Record
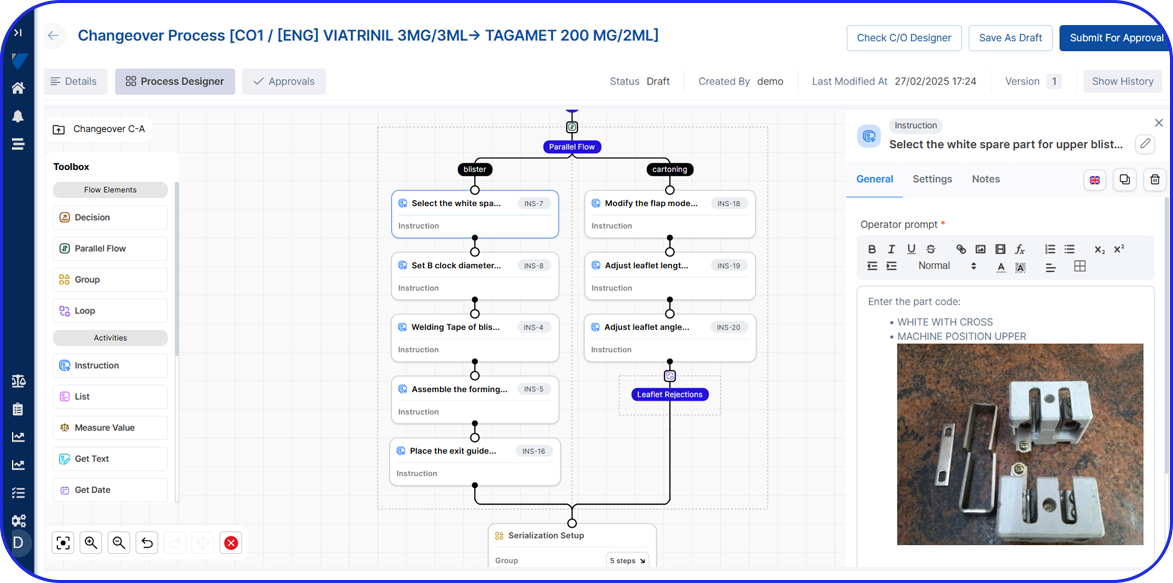
A Master Batch Record (MBR) is a detailed, standardized document that serves as the template and workflow for manufacturing a specific pharmaceutical product, specifying the required materials, equipment, processes, and critical production parameters to be recorded during batch execution.
It includes:
- Approved raw materials and quantities.
- Formulation details.
- Step-by-step processing instructions.
- Equipment requirements.
- In-process controls and critical parameters.
- Quality control and testing procedures.
- Packaging and labeling guidelines.
MBRs serve as the template for individual Batch Production Records (BPRs), which document the execution of each actual production run.
Whether managed on paper or digitally (as part of a Manufacturing Execution System, or MES), MBRs ensure that drug manufacturing is consistent, compliant, and traceable, in line with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Master Batch Records In Pharma
In the U.S., Master Batch Records (MBRs) are a regulatory requirement under the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP). In official FDA documentation, they are referred to as Master Production and Control Records. These records are mandatory under 21 CFR Part 211 and must be prepared for each unique formulation and batch size of a drug product.
What Is The Purpose Of A Master Batch Record For FDA?
According to CFR Part 211 mandates, the purpose of the Master Production and Control Record is to ensure uniformity from batch to batch and compliance with approved manufacturing procedures. These records must be in written form, “prepared, dated, and signed by one person and independently checked, dated, and signed by a second person.” Once approved, each batch must be produced according to the instructions laid out in the MBR to ensure product quality, safety, and regulatory compliance.
What Is Included In A Master Batch Record?
A Master Batch Record includes step-by-step instructions for every aspect of a product’s manufacturing components and procedures.
More specifically:
1. Name & Characteristics Of The Pharma Product
Product name, strength (i.e., the amount of active ingredient), and dosage form (e.g., tablet, capsule, patch). E.g. Phenoxymethylpenicillin X, 250 mg/tablet.
2. Drug Components
- Active Ingredients
Name and quantity (weight or measure) of each active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). - Full List Of Components
Names or codes of all active and inactive ingredients in the drug product. - Component Weight
Quantity (weight or measure) of each component, including any justified range of variation allowed during formulation.
Also includes a statement of any calculated component overages (e.g., for losses during processing).
3. Unit Weight
The total weight (or measure) per dosage unit (e.g., mL in an ampule, mcg in an inhaler).
This step requires an additional statement that mentions the estimated weight at different production phases.
4. Production Yield
The expected output after each process step, including the expected ranges (minimum and maximum percentages).
5. Drug Packaging
A detailed description of the drug packaging components (containers, closures, labels) and their materials. This document must include a copy of any product labeling on the carton, container, blister packs, bottles, etc., and must be signed and dated by the approver.
6. Manufacturing Instructions & Procedures
End-to-end manufacturing and control instructions, sampling and testing procedures, specifications, special notations, and precautions to follow:
- Work instructions for each station & stage of production – for machine and manual operations.
- Equipment specifications and cleaning requirements.
- Health and safety information during drug production.
- Quality control procedures, with details on sampling, testing, and acceptable test benchmarks.
- End product storage conditions and handling requirements.
Pharma Manufacturing Formula & Processing Instructions in The EU
Under EU GMP guidelines, as outlined in EudraLex Volume 4, Chapter 4, manufacturers are required to maintain approved, written Manufacturing Formula and Processing Instructions for each product and batch size.
This documentation is the EU equivalent of a Master Batch Record (MBR) in the U.S. and must include key details such as:
- Raw materials and their quantities.
- Equipment to be used.
- Processing steps and parameters (e.g., temperature, mixing time).
- In-process controls.
- Packaging and labeling instructions.
- All relevant specifications for manufacturing.
For pharmaceutical companies operating across both the U.S. and EU, or those holding regulatory approvals to sell products in both markets, it’s essential to align documentation between regions to ensure consistency and compliance.
Even manufacturers in semi-regulated regions can use EU GMP standards as a framework to develop robust internal MBRs, helping strengthen quality systems and prepare for global regulatory expectations.
Why Are Master Batch Records Important in the Pharma Industry?
It is evident that Master Batch Records MBRs play a crucial role in Pharma production.
First and foremost, MBRs serve as standardized guidelines, ensuring that all personnel follow consistent instructions, procedures, and controls, so every drug batch is manufactured the same way, every time. This consistency is essential for maintaining product quality and, ultimately, patient safety, whether it’s a single tablet or a spoonful of medicine.
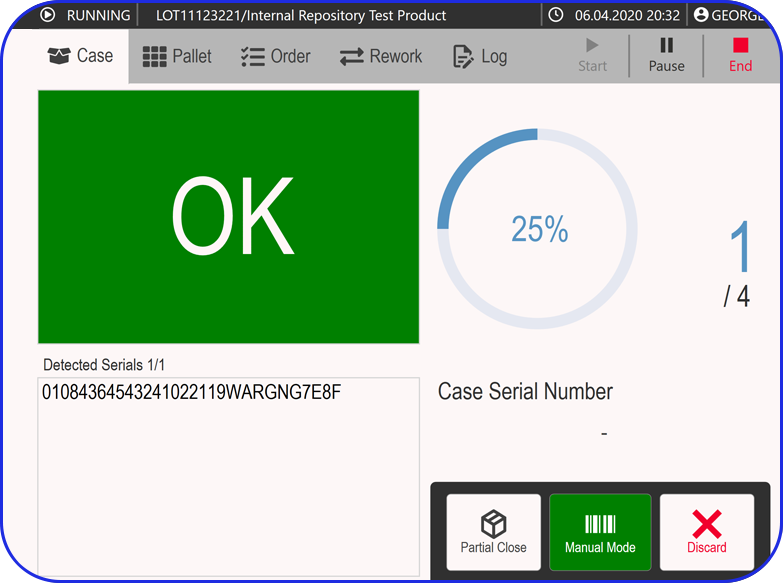
The MBR also functions as a template for creating Batch Production Records (BPRs). Each batch-specific record must align with its corresponding MBR, helping ensure completeness and compliance. Importantly, it also provides a framework for documenting and explaining any deviations that may occur during manufacturing.
Beyond the production floor, a well-prepared MBR serves a broader purpose. It provides transparency and traceability for regulatory authorities, internal departments, healthcare professionals, and even investors, acting as a foundation for demonstrating product quality and regulatory readiness.
While developing a comprehensive MBR can be a complex and time-consuming process, the knowledge it captures becomes a valuable, lasting asset, one that reinforces both operational excellence and regulatory confidence.
Benefits Of Digitizing Your Master Batch Records
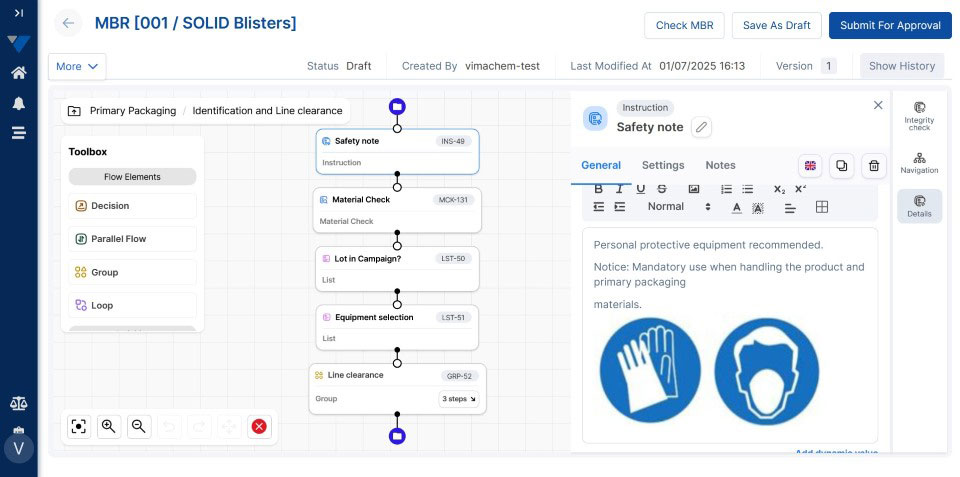
Historically, Master Batch records were compiled on paper or separate spreadsheets saved in a local or network server.
Outdated practices like these present various challenges that undermine product quality and production efficiency. Human errors, lost or unused data, inefficient processes, siloed production systems, and wasted time are just some of the problems hindering non-digital MBRs.
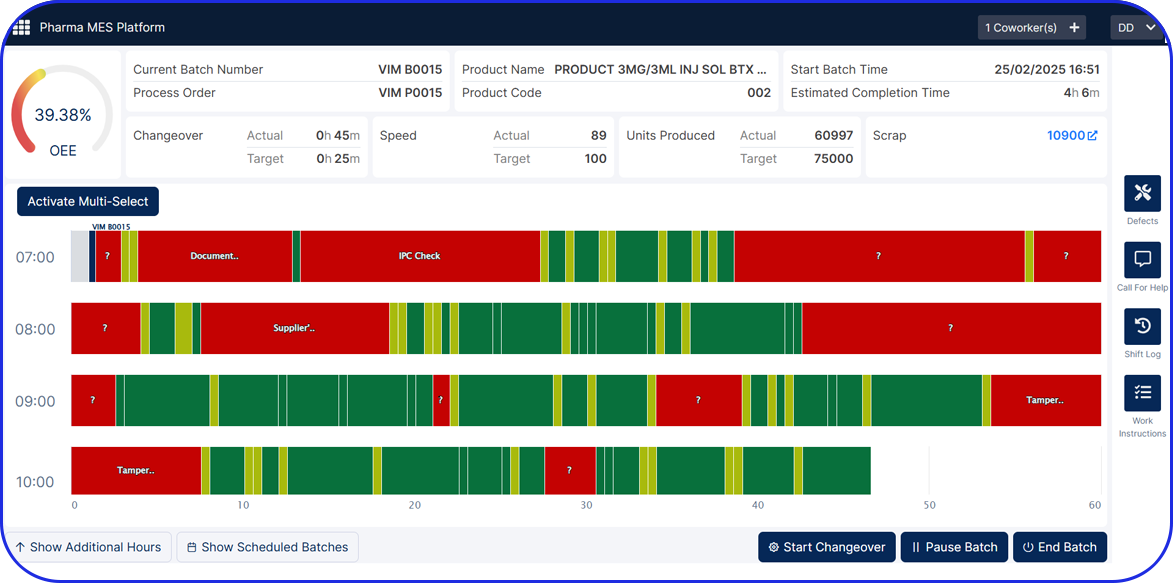
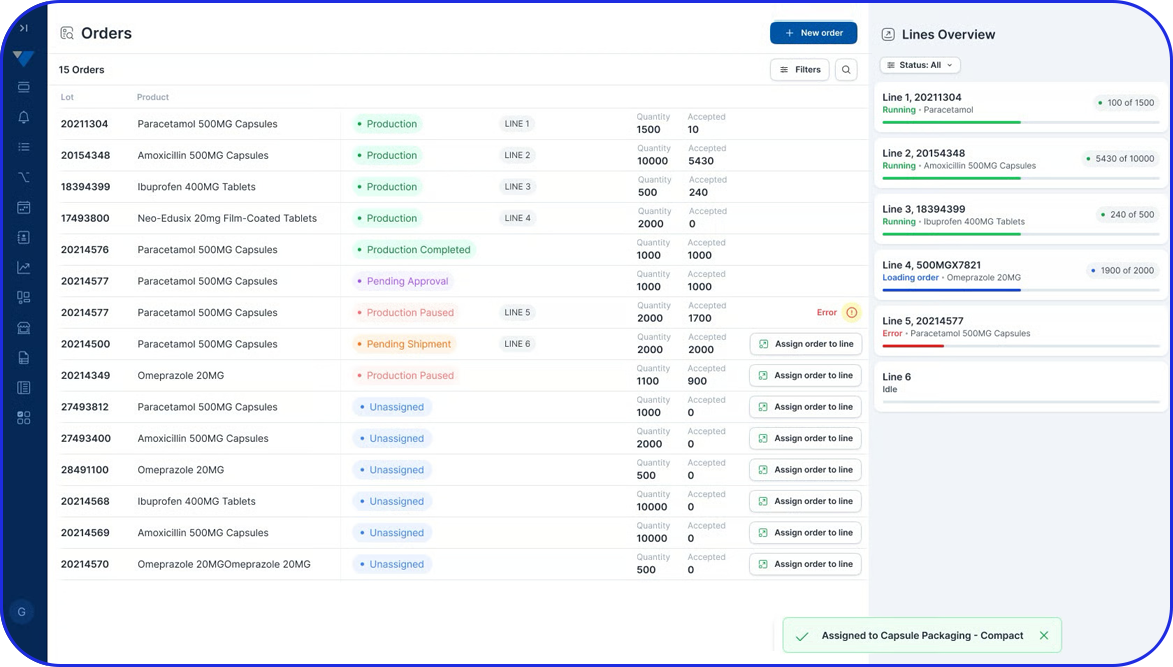
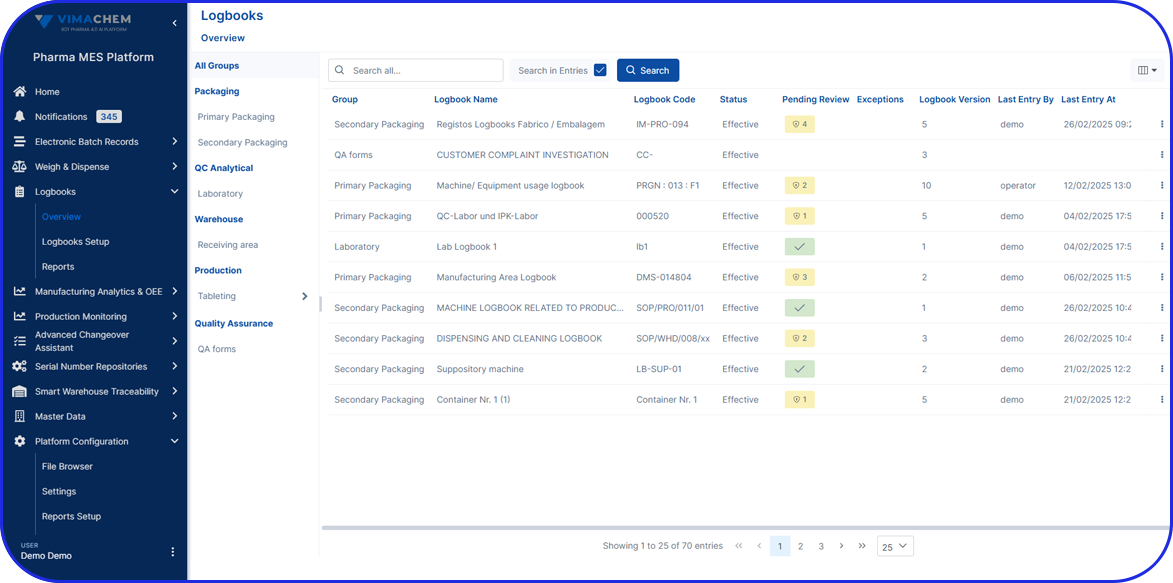
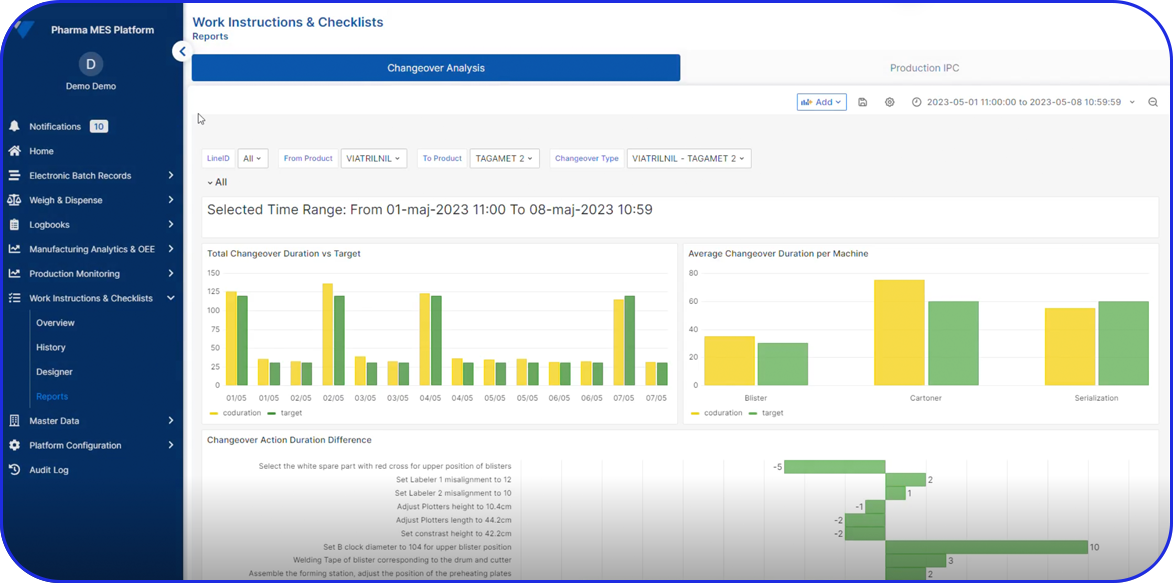
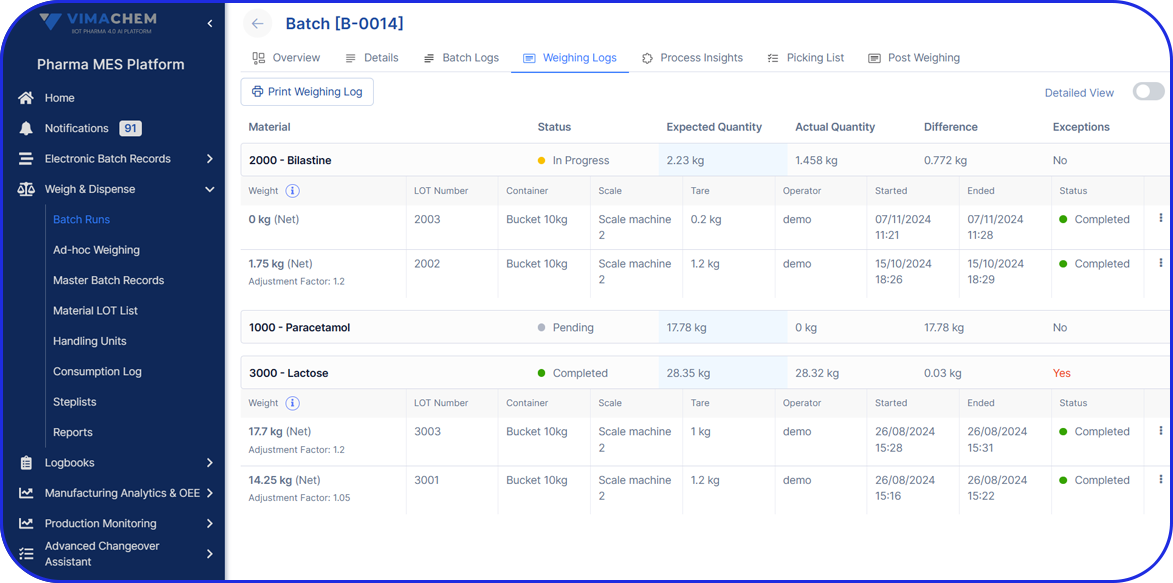
Today, cloud-based Electronic Batch Record (EBR) systems that house and manage Master Batch Records (MBRs) streamline manufacturing processes, accelerate batch execution, batch review based on exceptions only is possible and help ensure error-free drug production and strong regulatory compliance.
Digital Transformation & The Pharma Industry
In an era of paperless manufacturing, Vimachem’s digital EBR system, built exclusively for Pharma and Biopharma, helps manufacturers streamline production and adapt to changing regulatory requirements.
Plus, it accelerates the introduction of new products and enables process changes with minimal customization.