What Is Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance & Why Is It Important?
What Is Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance & Why Is It Important?
Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance (QA) is a comprehensive system designed around patient safety and pharma production optimization.
Following a pre-determined set of pharma QA processes and procedures ensures that pharmaceutical products consistently meet predefined quality standards and that both pharma manufacturing and supply-chain operations guarantee product reliability for consumers.
Effective Quality Assurance also helps pharma companies increase their profitability and market share and contribute to improving and enhancing drug development.
What Is Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance?
Pharmaceutical quality assurance (QA) is a framework of activities and processes that ensure pharmaceutical products are optimally manufactured and distributed. This means that they are safe to use throughout their lifecycle, maintaining their quality, consistency, and effectiveness.
In a nutshell, in QA, pharmaceutical firms start by defining their quality standards, which must be met in every detail during implementation. And to make the most out of their QA, pharma companies monitor all relevant KPIs to identify any drawbacks and discern any room for improvement.
In today’s data-driven environment, intelligent software such as MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) and Quality Management Systems (QMS) help industry professionals follow procedural guidelines and adhere to regulatory protocols, safeguarding product quality and ensuring compliance.

What Is Quality
Assurance In The
Pharmaceutical
Industry?
Quality Assurance (QA) Vs. Quality Control (QC) In The Pharmaceutical Industry
Quality Control and Quality Assurance in the pharmaceutical industry work together to secure drug safety. Simply put, QA establishes product quality, and QC checks and validates it.
QA Pharma - Definition
Quality Assurance in the pharmaceutical industry establishes quality standards in a wide range of activities – from drug development to manufacturing and from product transportation to storage and finally to retail.
Pharma companies proactively set their own production quality standards, incorporating explicit industry guidelines and regulatory compliance mandates.
QC Pharma - Definition
Quality Control (QC), on the other hand, validates that all standards set in Pharma Quality Assurance are met to the fullest.
In-house QC teams run rigorous testing and auditing on incoming substances and outgoing products, as well as manufacturing and transportation procedures. At the same time, health authorities conduct thorough inspections to verify compliance with regulatory standards.
In an effort to protect public health and ensure safety, Quality Control identifies and prevents defects or deviations during drug manufacturing, shipping, shelving, and selling.

- Establish and maintain SOPs and quality systems
- Ensure compliance with cGMP, regulatory standards (FDA, EMA)
- Conduct internal audits and inspections
- Oversee training and qualification programs
- Review and approve validation protocols
- Manage documentation and change control
- Handle deviation and CAPA processes
Supplier and contract manufacturer qualification

- Perform raw material, in-process, and final product testing
- Operate analytical instrumentation (e.g., HPLC, GC, FTIR)
- Conduct stability studies
- Prepare certificates of analysis (CoA)
- Maintain lab records and test data integrity
- Calibrate and maintain laboratory equipment
- Support batch release decisions
- Investigate test failures and OOS results
Why Is Quality Assurance Important In Pharmaceuticals?
Quality Assurance is an integral part of pharmaceutical production and supply chain.
Here are a few reasons why:
- Assures product quality specifications are met.
- Oversees that every batch follows regulatory guidelines.
- Identifies and manages risks from production to consumption.
- Foresees and minimizes potential issues.
- Enhances product quality on an ongoing basis.
- Meets customer expectations, e.g. price, taste, convenience.
- Promotes a culture of continuous improvement.
- Sustains collaborations in cross-border supply chains and secures access to global markets.
- Optimizes processes and helps improve profitability.
- Promotes data-driven decisions and valuable root-cause analysis, significantly benefiting pharma productivity as a whole.
Indeed, pharma QA affects every aspect of drug production and logistics.
"Continuous improvement fosters pharma quality on every level."
Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Touches Every Stage Of The Product Lifecycle
Quality Assurance in pharma is not a standalone process but a comprehensive system integrated into every phase of a medicinal product’s lifecycle – from the earliest stages of R&D to dispensing or administration to patients – and beyond:
Drug Research
Preclinical Stage: The initial phases of R&D require, among others, accurate data collection, adherence to ethical standards, and the establishment of a strong foundation for upcoming clinical trials.
Drug & Formulation Development
Clinical Trials: At this stage, pharmaceutical quality procedures prioritize participant safety and ensure the integrity of trial data – always in compliance with applicable regulatory protocols.
Production Of Pharmaceuticals
Manufacturing: Pharma companies abide by Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs), continuously checking and inspecting drug substances, processes, and product batches in order to meet all pre-determined standards.
Pharma Distribution
Distribution: Pharma products are shipped and stored following specific guidelines to maintain quality. For instance, in temperature-sensitive drugs – such as vaccines – detailed transportation and cold-storage protocols prevent spoilage and unnecessary medicine waste.
Pharma Post-Marketing Surveillance & Evaluation
Post-Distribution: Even after a drug reaches the market, quality checks in medical units and pharmacies are strategically conducted in order to identify and mitigate potential safety issues due to unsuitable storage conditions or improper use. Moreover, pharmaceutical firms assess new clinical findings and monitor drug usage data in an effort to enhance drug efficacy, reduce side effects, or, conversely, detect batch quality defects or unforeseen health risks, enabling rapid product recalls through tracking and tracing of individual drug packages.
This holistic integration of QA in the pharmaceutical industry guarantees that every single product item meets the highest standards at every step of its journey.
Quality Assurance Core KPIs - Pharma
Compliance & Documentation
- % SOPs past due for review
- % of GMP documentation errors
- Deviation closure on time (%)
- Audit findings per audit (internal/external)
- Regulatory inspection readiness status
Process Performance
- Batch record review cycle time
- Right first time (RFT) rate – % of batches with no errors
- % of process deviations per batch
- Change control implementation lead time
- QA review lead time (for documents, events, validations)
Quality Events & Risk
- Number of deviations / CAPAs per month
- % CAPA completed on time
- Recurrence rate of deviations
- Product complaint rate (per 1000 units)
- Supplier quality issues / audits passed
“Why it matters” – KPIs help ensure consistent product quality and readiness for audits/inspections.
How To Meet Pharmacy Quality Assurance Goals
As a pharmaceutical company, to achieve your QA objectives, you should:
1. Develop A Quality Policy And Quality Assurance Plan
Start by establishing a clear policy that outlines your company’s commitment to quality and compliance, focusing, above all, on benefiting patients.
Then, develop a QA plan specifying procedures, responsibilities, and quality standards.
Keep on evaluating and updating your processes along with your team.
2. Work On A Quality Risk Management (QRM) Plan
QRM is vital in pharma, as it helps identify and mitigate potential risks at every stage of the product lifecycle. Regular risk assessments and evaluations strengthen your QRM plan even more.
3. Train And Empower Employees
Continuous training ensures that the entire staff understands and adheres to your Quality Assurance protocol and all regulatory standards.
Your most experienced and skilled quality professionals can substantially contribute to upscaling operations. So, it’s worth investing in ongoing employee learning, development, and inspiration.
Continuous improvement fosters quality on every level.
4. Leverage State-Of-The-Art Tools
In today’s digital transformation landscape and with impactful initiatives like Pharma 4.0, pharmaceutical companies have a wide array of tools to leverage the power of AI, cloud computing, automation, and other cutting-edge technologies.
Such integrations provide new ways to efficiently handle and utilize data, streamline end-to-end processes, and optimize decision-making.
The result? Reaching very high levels of Quality Assurance – seamlessly.
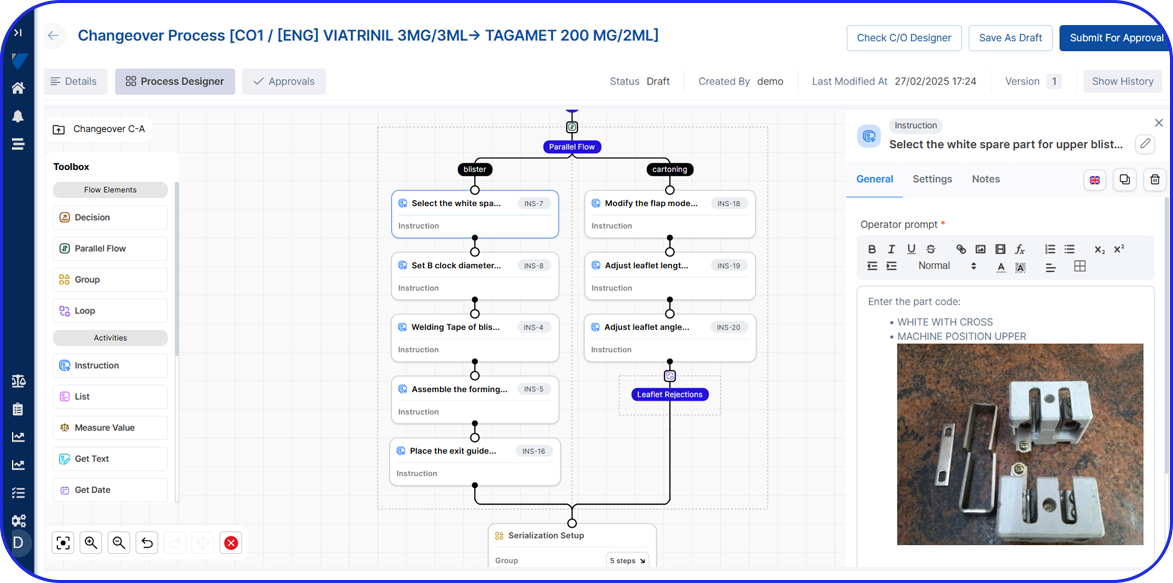
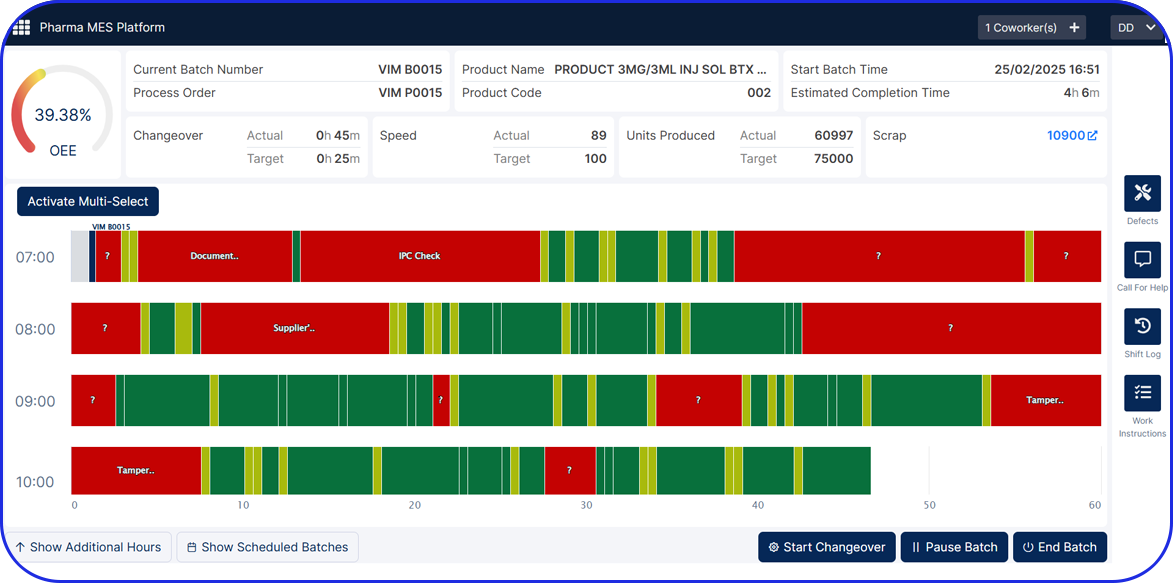
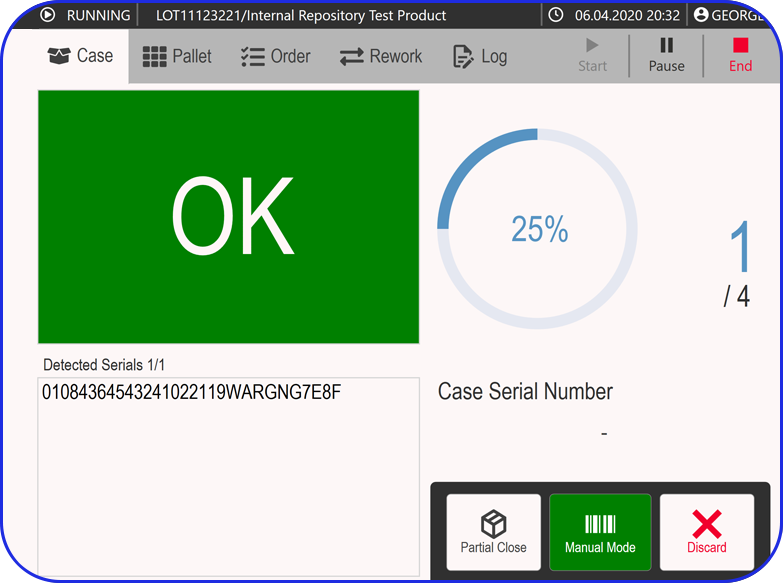
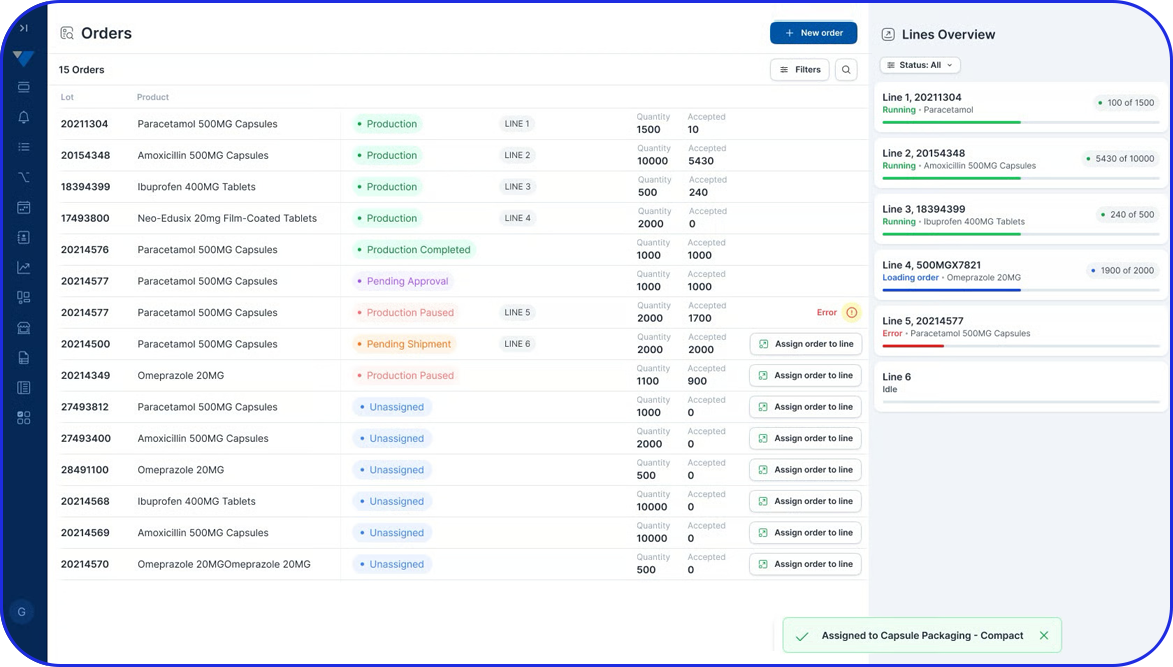
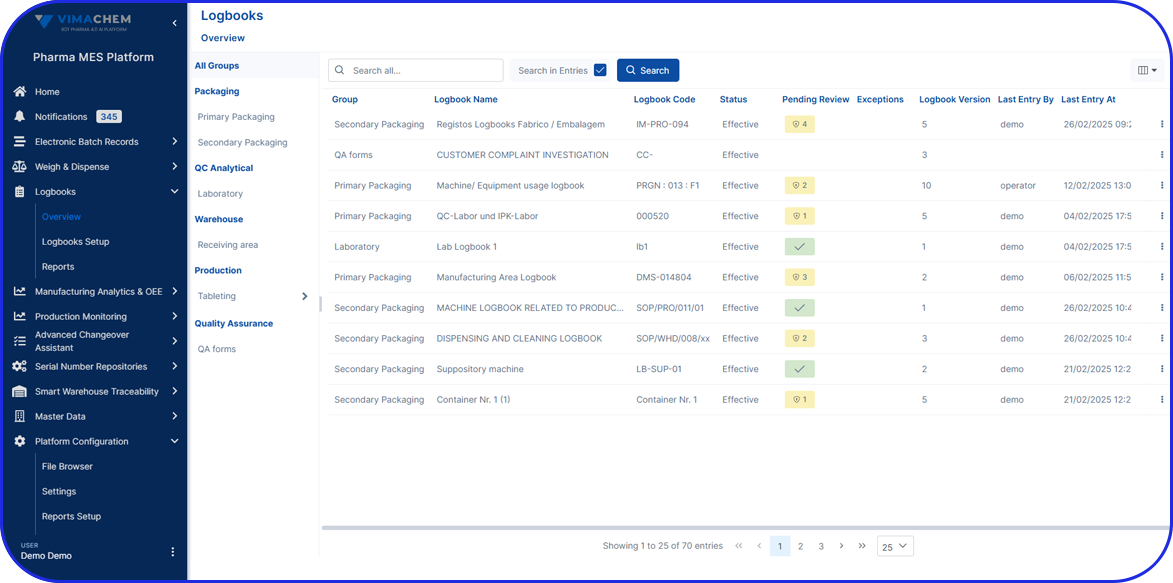
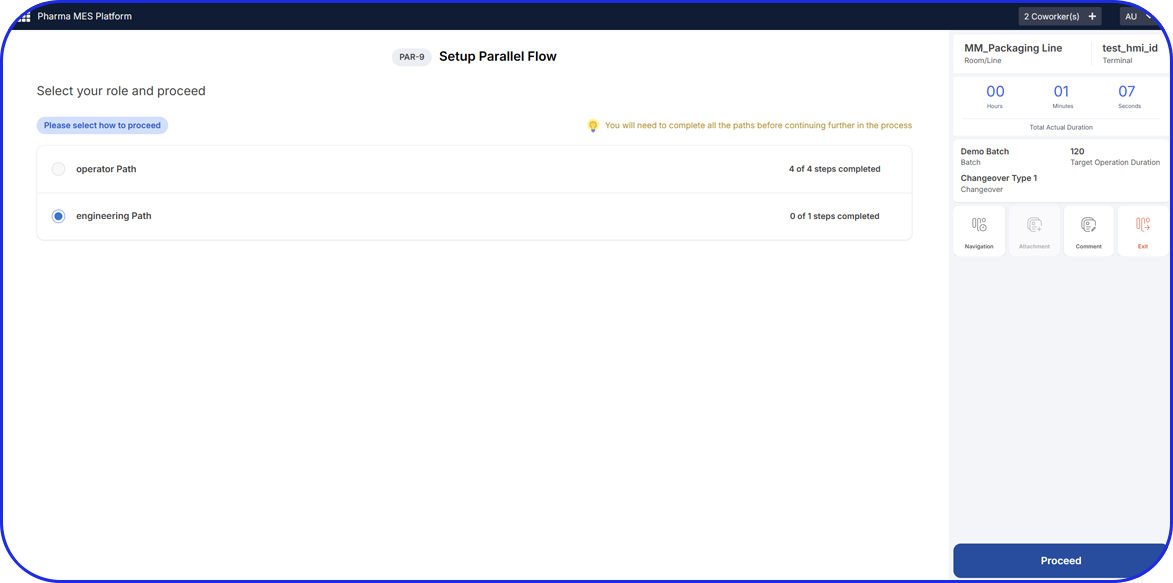
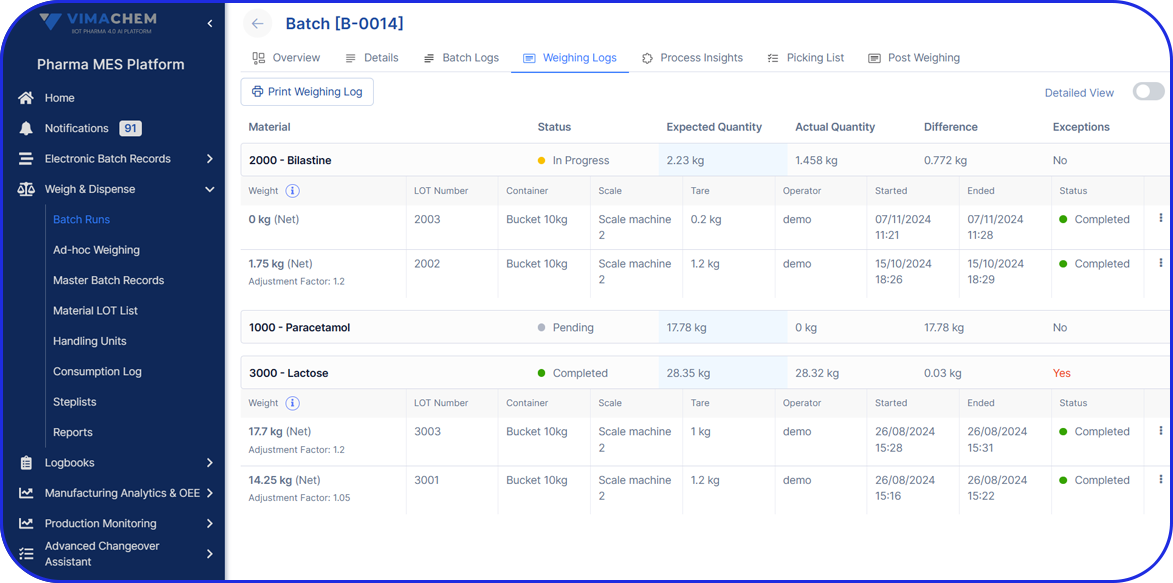
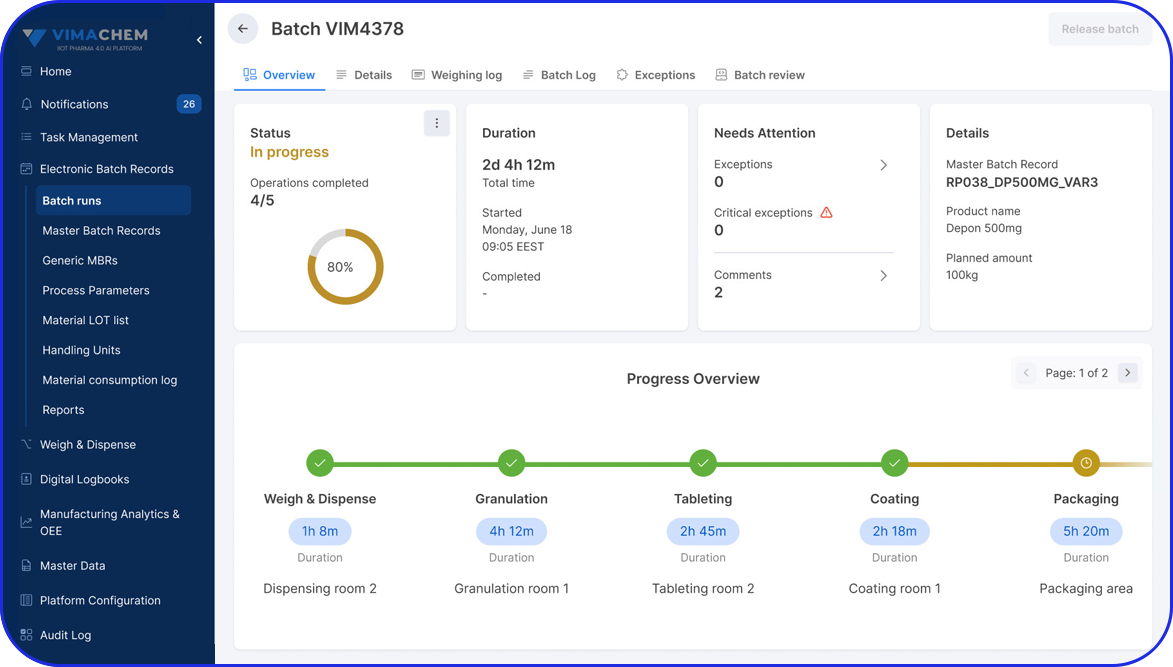
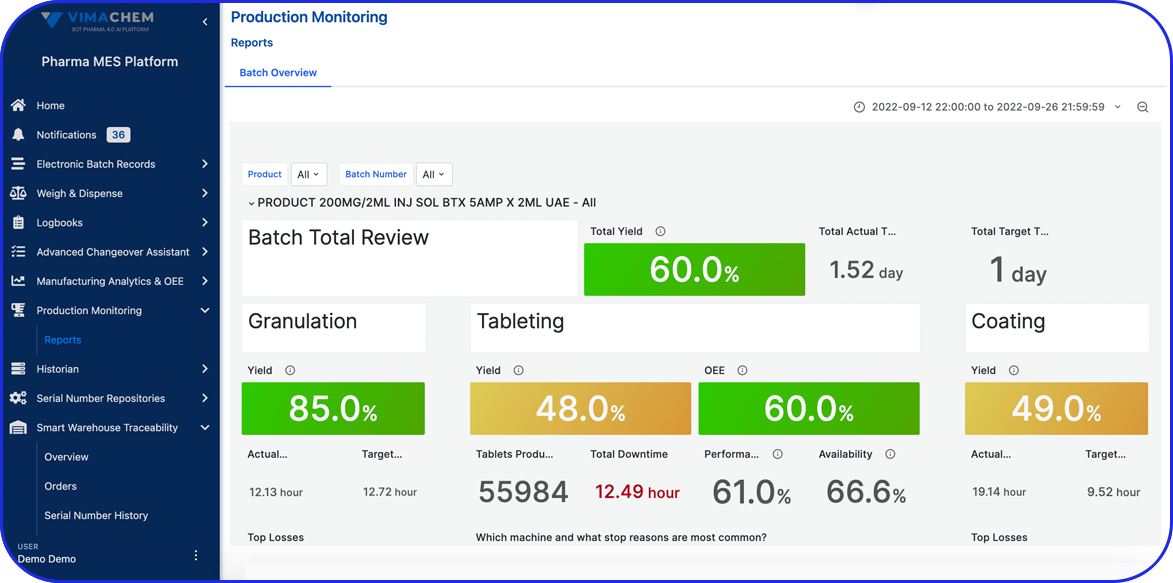
Admittedly, comprehensive pharma MES software like Vimachem’s IIoT AI Pharma Platform empower industry professionals to optimize processes and profoundly utilize assets and functions like:
- Digital forms and logbooks
- Electronic batch records (EBR)
- Weigh and Dispense
Document Management - Manufacturing analytics and OEE
- Machine data connectivity – and more.