Pharmaceutical Industry Trends: Innovations Shaping the Future
Pharmaceutical Industry Trends: Innovations Shaping the Future
21 CFR Part 11 Compliance: Guidelines & Checklist For Pharma
21 CFR Part 11 Compliance: Guidelines & Checklist For Pharma
The digital transformation in the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries embraces electronic systems for managing critical data. Easier said than done, dealing with electronic data in such sensitive fields falls under strict regulatory compliance regulations.
At the heart of this complex landscape lies 21 CFR Part 11, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) definitive regulation for electronic records and electronic signatures.
More than compliance guidelines for pharmaceuticals, these regulations enhance data security and operational integrity.
What Is FDA 21 CFR Part 11?
21 CFR Part 11 is an FDA regulation issued in 1997. It specifies the requirements for digital documents and signatures and defines the criteria that make electronic records and electronic signatures trustworthy and reliable, including strict security standards.
This regulation applies to industries regulated by the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) and to all electronic records created, modified, maintained, archived, retrieved, or transmitted throughout an organization’s regulated operations.
It also applies to electronic records submitted to the FDA under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act and the Public Health Service Act, even if those records are not explicitly mentioned in other agency regulations.
Core 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance Guidelines For Pharma - Summary
To stay compliant with 21 CFR Part 11, pharmaceutical organizations must adhere to specific FDA requirements across several key areas.
To name a few:
System Validation
All systems that create or manage electronic records should consistently perform as intended. They must be accurate and reliable, and capable of distinguishing between valid and invalid (or altered) records.
Audit Trails
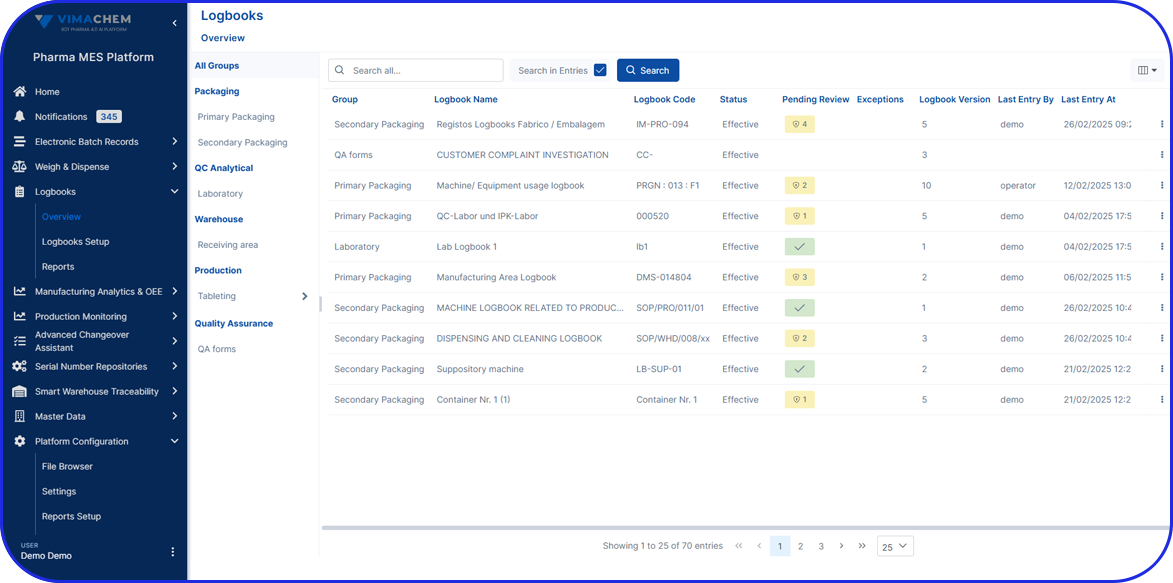
A core tool for traceability, audit trails require secure, system-generated, time-stamped records that document operator entries and actions regarding the creation, modification, or deletion of digital records. Audit trails must be retrievable and available for FDA review and export throughout the required retention period.
Electronic Signatures
Each signature must be uniquely assigned to an individual and include the signer’s printed name, the exact date and time, and the purpose of the signing (e.g., approval or review). It should also be permanently linked to its corresponding electronic record to prevent falsification.
Choosing A 21 CFR Part 11 Compliant Software
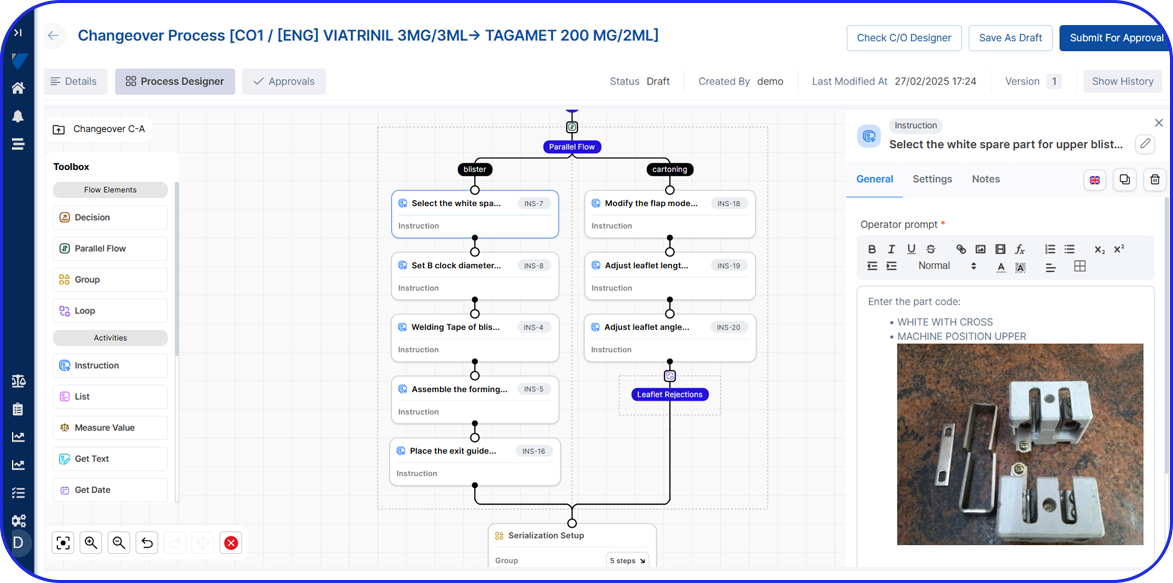
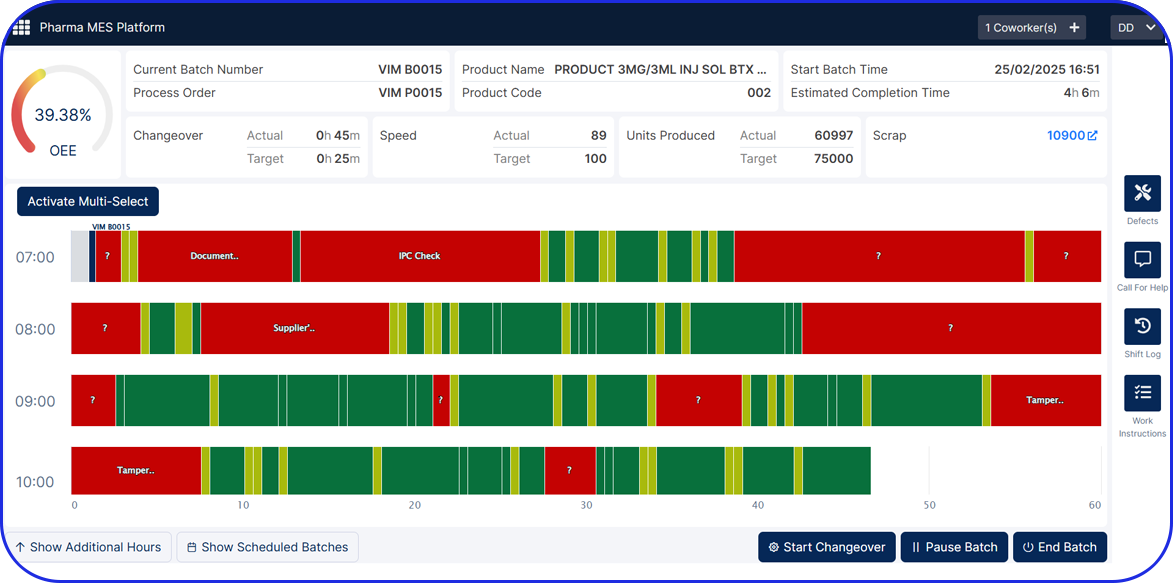
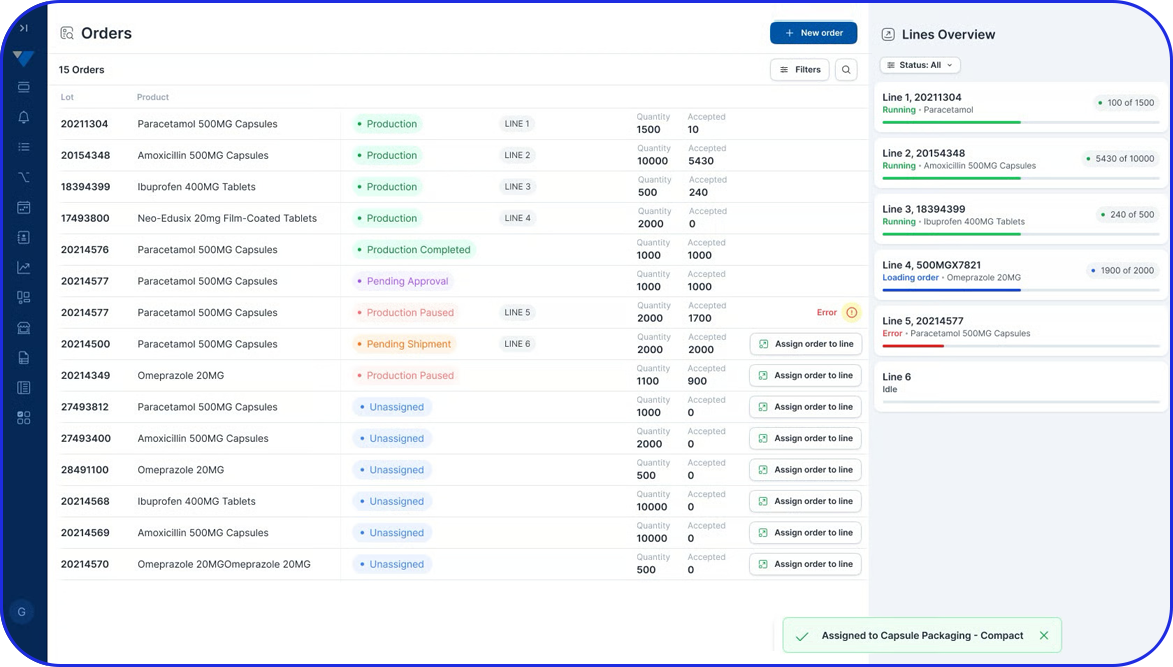
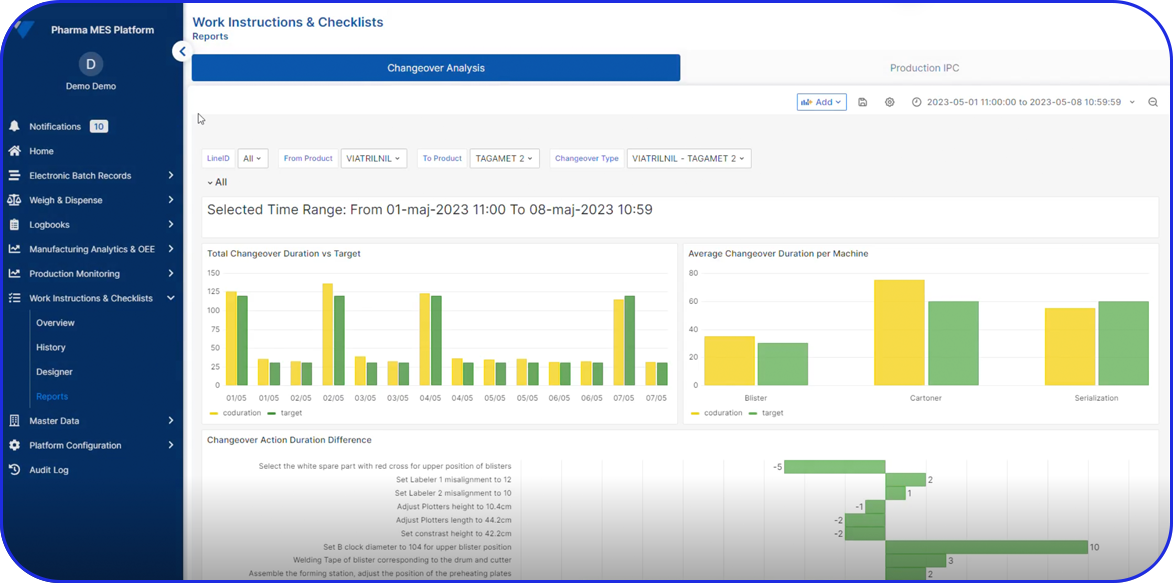
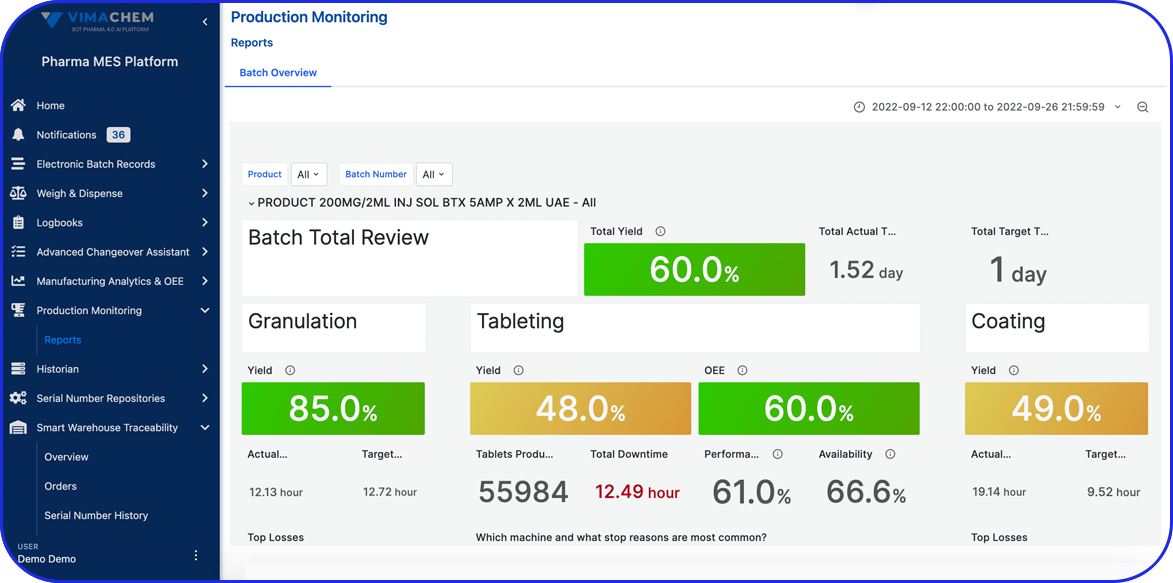
Many organizations use specialized 21 CFR Part 11 compliant software, such as Electronic Quality Management Systems (eQMS), cloud-based electronic Batch Records (eBR), or intelligent Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES).
These systems offer numerous advanced features like detailed, fully traceable audit trails, robust data security, and password-protected or biometric electronic signatures, in order to adhere to the latest integrity and compliance standards.
As a pharma manufacturer, you should opt for a trusted solution with a proven track record of security and efficiency, such as the Vimachem MES platform and eBR module, because, at the end of the day, your organization remains ultimately responsible for ensuring its own compliance.
21 CFR Part 11 Compliance Checklist For Pharmaceuticals
Here’s an initial checklist to guide your compliance efforts:
1. System Validation
- Is your system validated, reliable, and consistent to ensure data accuracy and integrity?
- Can your system detect invalid or tampered records?
- Does your system enforce the sequence of steps or events (process control) if crucial?
- Can your records be retrieved and exported quickly and reliably (throughout the retention period)?
- Is access to the system restricted to authorized users only?
- Are users and personnel properly trained and aware of their accountability as outlined in your internal policies?
2. Audit Trails
- Does your system generate secure, detailed, and time-stamped audit trails that record operator entries, actions, and the sequence of all events, e.g., creation, modification, removal, revision, or change control?
- Are audit trails implemented for all critical records and retrievable throughout the retention period?
- Are your audit trails available for evaluation and copying by the FDA?
- Is there an official change control procedure for system documentation?
3. Electronic Signatures
- Is each electronic signature unique to a single individual?
- Is an individual’s identity thoroughly verified and submitted to the FDA before assigning an electronic signature?
- Has it been verified that biometric and non-biometric signatures can only be used by their genuine owner?
- Are signatures comprised of a minimum of two elements (e.g., ID code/password) at all instances, regardless of the context or session?
- Does each electronic signature link to its respective electronic record?
4. Record Retention
- Can the system generate accurate and complete copies of records, ready for review and automated export in commonly used formats (PDF, XML, or SGML)?
- Do record retention policies apply equally to electronic and paper systems?
5. Access Security
- Are user credentials unique, regularly updated, and protected against duplication?
- Are there procedures in place to revoke system access in cases where codes/passwords are compromised, employees leave/change roles, devices are stolen, etc.?
- Is there a procedure for identifying and reporting any unauthorized or unlawful use, as well as notifying security?
- Is there regular device performance testing to ensure proper functionality?
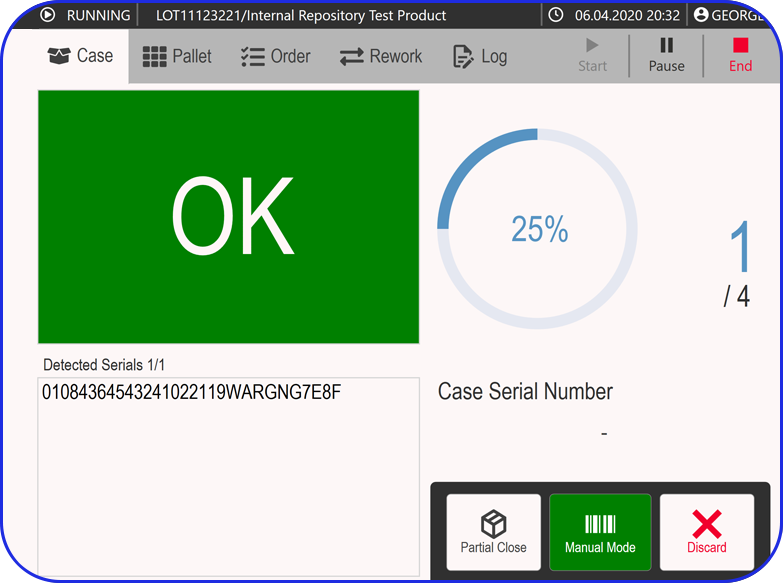
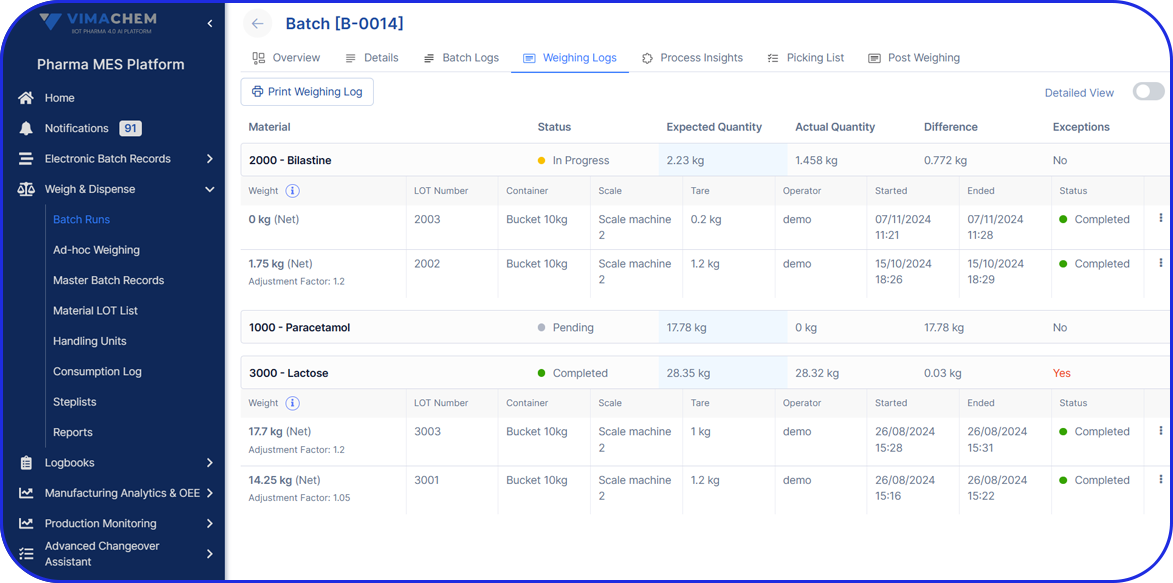
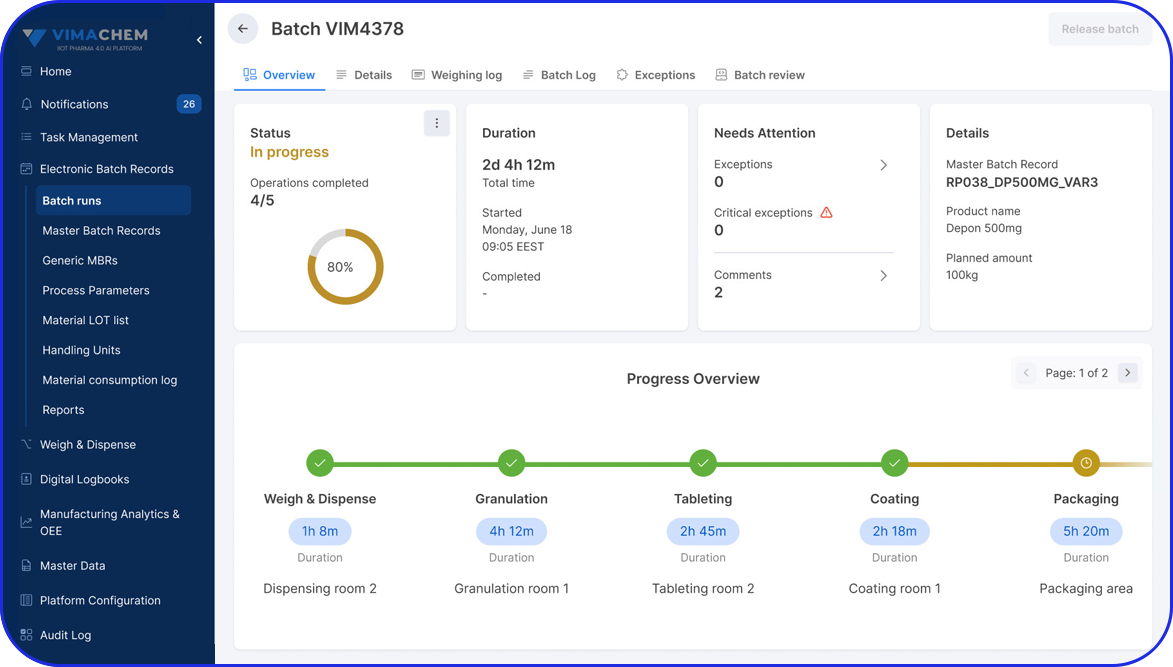
How Do Electronic Batch Records (eBRs) Help Companies Comply With 21 CFR Part 11?
Heading towards end-to-end digitalization in pharma, electronic Batch Records (eBRs) with integrated electronic signatures document and track the entire production process to the finest detail.
Modern eBR platforms go beyond mere record-keeping; they act as an essential tool, integrating with other core systems like your Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Manufacturing Execution System (MES), enhancing efficiency and transparency.
As a leading, cloud-based platform built exclusively for pharma and biopharma, the Vimachem eBR software provides a secure, validated, and auditable data and process environment.
Thanks to its built-in compliance with FDA, GMP, and 21 CFR Part 11-ready features, the Vimachem eBR reduces deployment timelines by at least two months while ensuring full compliance from the initial rollout.
Facilitating the transition to paperless manufacturing, the Vimachem solution enhances data integrity, quality, and traceability across production processes, helping your business stay compliant and scale with ease.
Technological Advancements Are The Key Trends In The Pharmaceutical Industry
Nowadays, current pharma trends are all about efficiency, optimization, compliance, and personalization on every level: from R&D to distribution and from ground-breaking pharmaceuticals to proactive care.

Top 5 Pharma Trends – Infographic