What is Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing? Key Advantages
What is Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing? Key Advantages
Pharmaceutical contract manufacturing allows Marketing Authorization Holders (MAH) to outsource part or all of their production to specialized third-party manufacturers. This popular model offers a wide range of strategic and operational benefits.
This article explores the fundamentals of pharmaceutical contract manufacturing services and highlights their key advantages.
What is Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing?
Pharmaceutical contract manufacturing is a model in which pharmaceutical companies outsource part or all of their drug production activities to specialized third-party providers. A Contract Manufacturing Organization (CMO) may be responsible for producing active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), the biologically or chemically active components of medications, as well as handling drug formulation and manufacturing the final dosage form (e.g., oral solid dosage, injectables). Many CMOs also manage downstream processes such as coating, packaging, and labeling.
These manufacturers operate strictly according to the formulation, process specifications, and regulatory requirements provided by the client. They must comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other industry regulations to ensure product quality and patient safety.
Depending on the contractual arrangement, the brand owner may supply the raw materials (including APIs and excipients), or the CMO may handle sourcing. In some cases, companies outsource only the packaging and labeling stages to a specialized Contract Packaging Organization (CPO), particularly for over-the-counter (OTC) products, where labeling accuracy and regulatory compliance are especially critical.
Some pharmaceutical companies also work with Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs), which offer a broader range of services spanning drug development, clinical trial material production, and commercial-scale manufacturing, often acting as end-to-end partners from formulation to final packaging.
Together, CMOs, CDMOs, and CPOs form the backbone of pharmaceutical outsourcing, allowing companies to remain agile, reduce costs, and accelerate time-to-market.
CMO Contract Manufacturing: Facts and Figures
Pharmaceutical contract manufacturers are essential partners in the global drug supply chain, contributing to the production of a wide range of pharmaceutical products, from tablets and capsules to injectables, ointments, and more.
In fact, the global pharma contract manufacturing market depicts a steep upward curve. Valued at USD 172 billion in 2023, it is expected to reach approx. USD 330.52 billion by 2033, attaining a 6.80% CAGR from 2024 to 2033.
Today, North America holds the largest share of the contract-manufacturing pharmaceutical market – expected to reach approx. USD 84.07 billion by 2033 at a 6.90% CAGR.
Benefits of Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing
By outsourcing some or all of the activities of drug production processes, pharmaceutical companies can focus their attention and resources on what they do best. In other words, research and development.
Beyond helping bring new and more effective medicines to market, pharmaceutical contract manufacturing offers a range of additional benefits.
Among them:
Cost Effectiveness
Third-party manufacturers enable pharmaceutical companies to significantly reduce operational costs, such as those related to specialized personnel, equipment maintenance and upgrades, and facility management. This cost-efficiency often translates into lower production expenses and improved profit margins.
Indeed, biotech firms can save up to 30% in capital expenditures and about 25% in production costs by partnering with pharmaceutical contract manufacturers.
Risk Mitigation
CMOs in pharma are always up-to-date with current regulatory compliance and quality assurance regulations and have a thorough understanding of all federal laws affecting the production of pharmaceuticals – minimizing the risk of corrective actions or recalls.
They are also experts in drug production management and provide contingency plans, thus avoiding production delays and safeguarding against supply chain disruptions.
Profound Expertise
As specialists in pharmaceutical production, contract manufacturers leverage cutting-edge technology and streamlined processes to maximize efficiency while ensuring strict adherence to quality and regulatory standards.
Scalability
To respond to fluctuating market demand, third-party manufacturers offer flexible production capacities that can be scaled up or down as needed. This agility reduces costly slowdowns and accelerates time to market, benefiting both small and large pharmaceutical companies.
Access to New Markets
Many contract pharmaceutical companies operate on an international scale, giving them deep knowledge of diverse national regulatory requirements. They often maintain local networks and infrastructure, enabling their partners to navigate compliance and enter new markets more quickly and efficiently.
Given the constantly evolving nature of pharmaceutical regulations, staying current and compliant is essential, not only to maintain market access but also to ensure patient safety at every stage of the product lifecycle.
"You've got to optimize, you've got to find efficiencies, you've got to figure out where you can remove cost to keep the lights on. But why do you do that, those savings can actually translate into your future expansions."
Chris Preti, CEO of Jubilant HollisterStier Contract Manufacturing Services. Exploring CMO Strategies, PharmaTech magazine
What are the Regulatory Requirements for Contract Manufacturing In Pharma?
Regulatory requirements for contract drug manufacturing vary by country. In the United States, for example, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requires, among other things, that Quality Agreements be established between the pharmaceutical company and the Contract Manufacturing Organization.
These agreements clearly define each party’s responsibilities regarding manufacturing operations, quality control, documentation, deviation management, and communication protocols.
While the pharmaceutical company retains ultimate responsibility for product quality and regulatory compliance, both parties must ensure that all manufacturing processes are validated, and that operations are closely monitored and controlled in accordance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
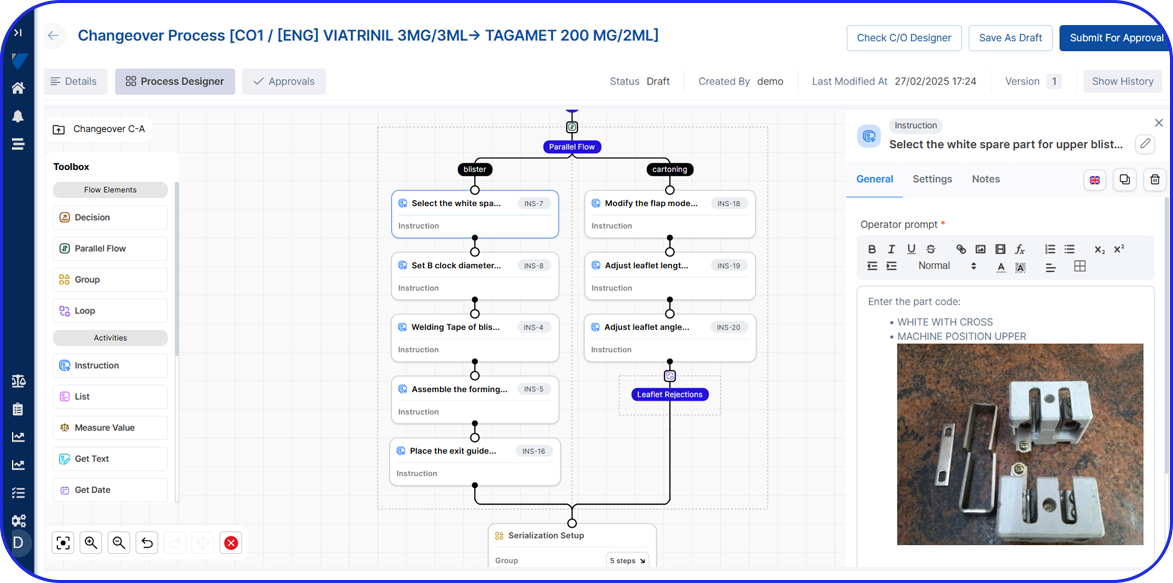
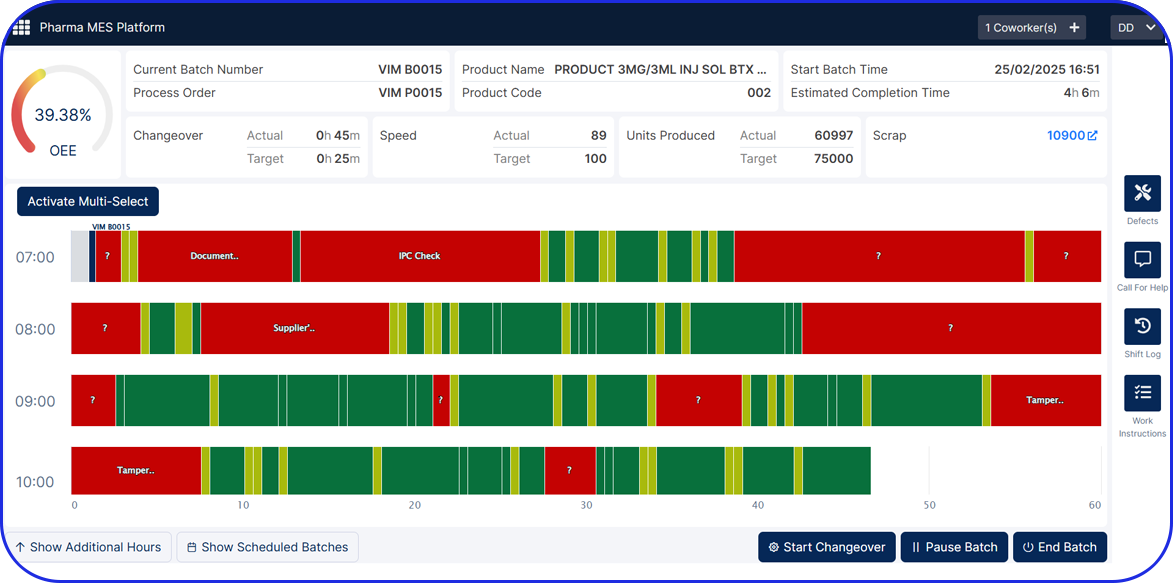
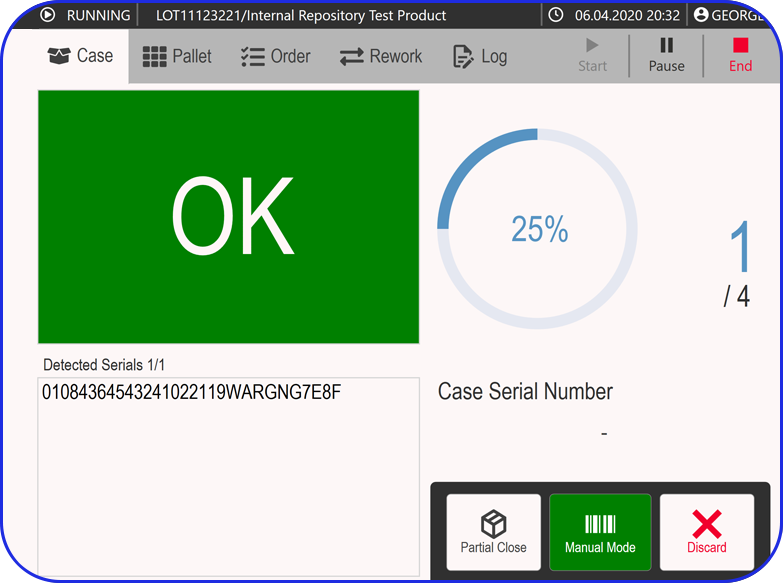
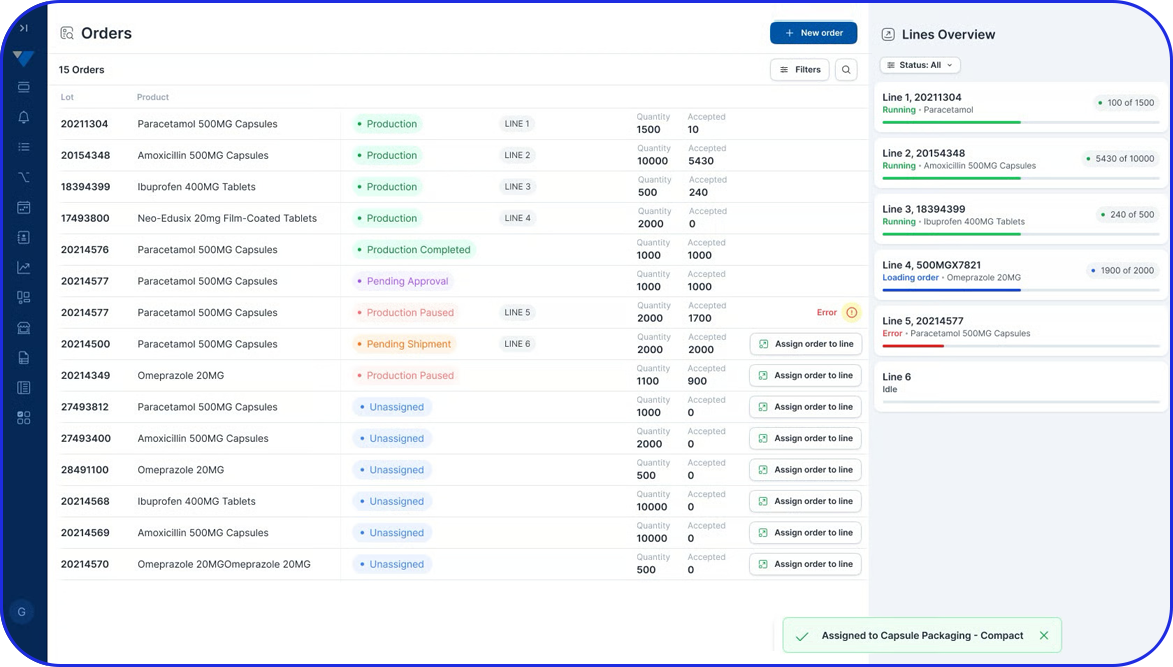
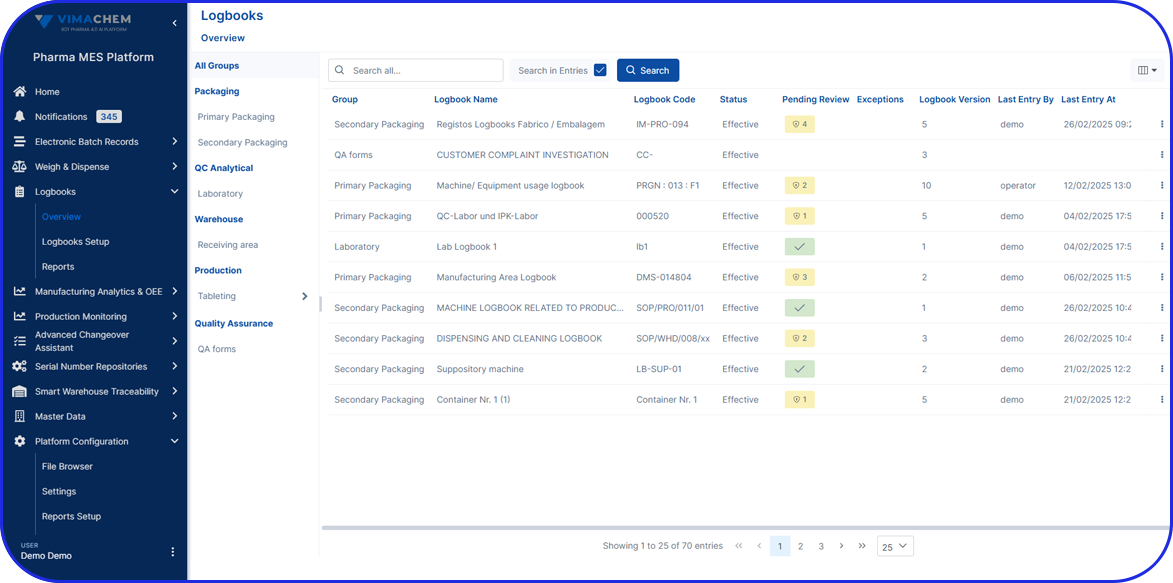
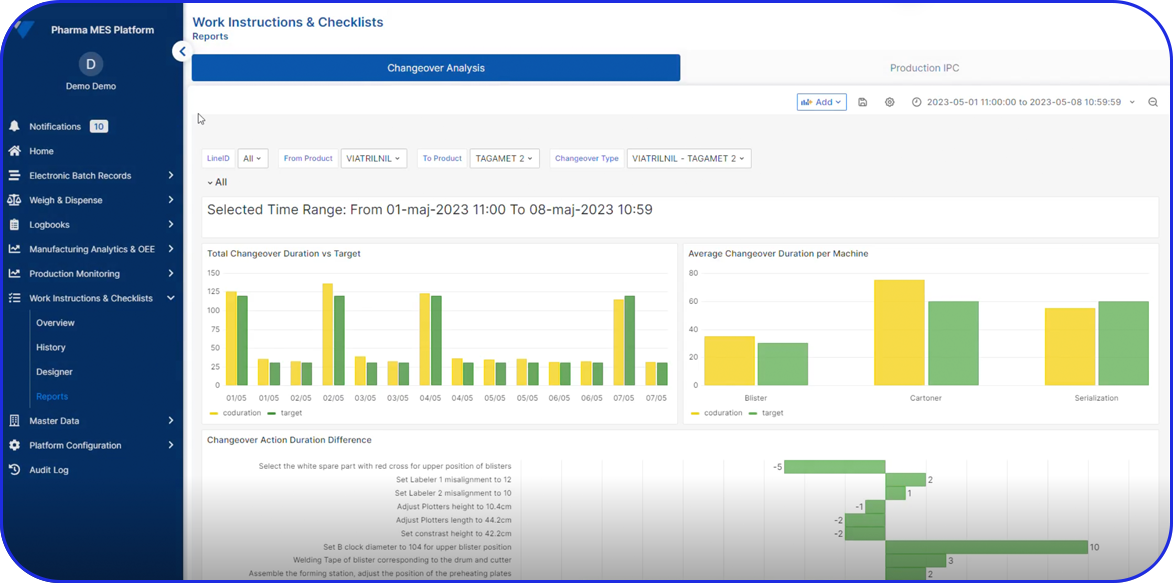
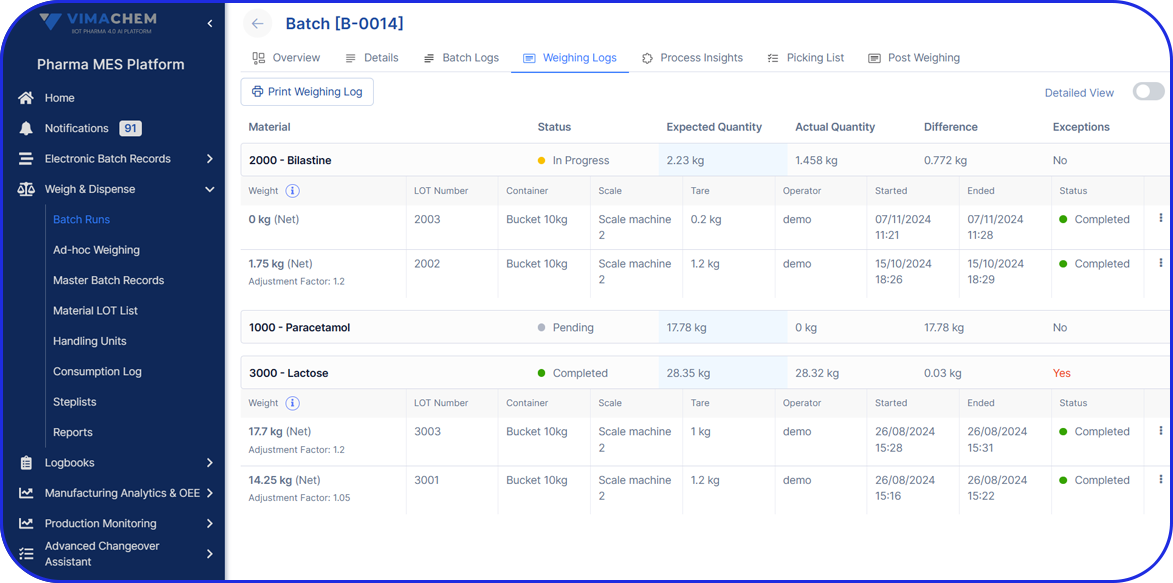
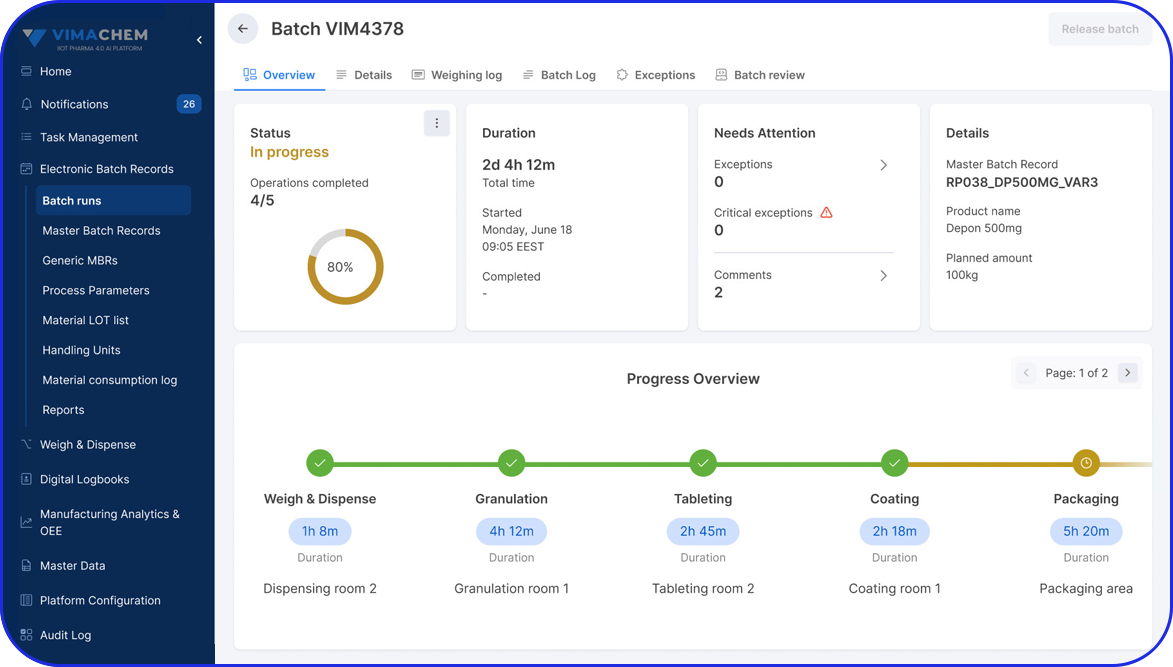
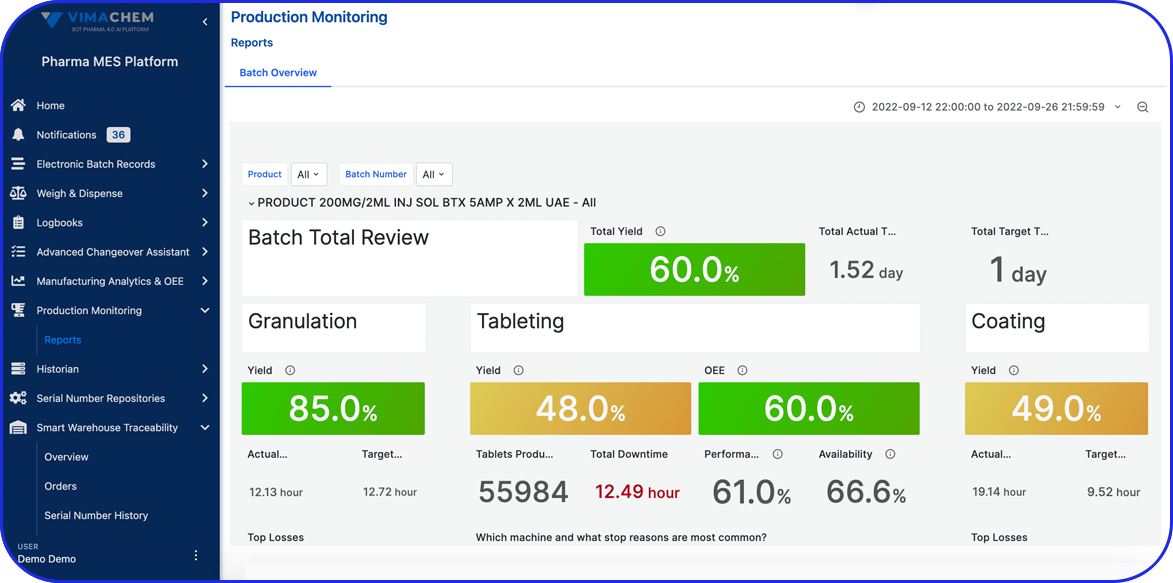
In this highly regulated environment, Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) play a critical role in streamlining production, ensuring traceability, and supporting compliance with regulatory standards.
How AI Pharma MES Systems Support Manufacturing Operations
Vimachem’s AI Pharma MES enables CMOs and pharmaceutical companies to ensure regulatory compliance, increase efficiency, and accelerate time to market, all while maintaining full control over production operations.
Designed specifically for Life Sciences CDMOs and CPOs, Vimachem’s Manufacturing Execution System (MES) incorporates AI, IIoT, and Pharma 4.0 principles so that pharmaceutical firms and their manufacturing contractors can scale with greater ease and flexibility.
Transform your operations
FAQ: More Information on Pharma CMOs
What is a CMO in Pharma?
In the pharmaceutical industry, CMO stands for Contract Manufacturing Organization. A CMO is a third-party provider that handles the production of drug substances (APIs), formulation of finished drug products, and/or packaging and labeling, all based on the specifications provided by the sponsoring pharmaceutical company.
CMO vs. CDMO vs. CPO: What's the Difference?
- A CMO focuses on manufacturing drug products in line with client specifications.
- A CDMO (Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization) offers end-to-end services, covering everything from formulation and process development to clinical and commercial manufacturing, and sometimes even packaging, essentially acting as an extension of the pharma company’s operations.
- A CPO (Contract Packaging Organization) specializes exclusively in packaging, labeling, and serialization of drug products. CPOs often work with CMOs or directly with pharma companies to prepare products for market release, especially in highly regulated environments like OTC or international markets.
What does a CMO Do?
A CMO (Contract Manufacturing Organization) provides contract manufacturing services, which typically include:
- API synthesis or sourcing.
- Drug formulation based on client-supplied specifications.
- Production of solid, liquid, or injectable dosage forms.
- Packaging and labeling.
Pharma companies may rely on CMOs when they lack in-house manufacturing capabilities or prefer to outsource production for cost or scalability reasons.
What Does A CDMO Do?
A CDMO (Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization) offers a broader scope of services, including:
- Drug development and formulation.
- Analytical and stability testing.
- Tech transfer and scale-up.
- Clinical trial material production.
- Commercial-scale manufacturing.
CDMOs are often chosen by pharma firms looking for an integrated development and production partner.
What Is a CPO in Pharma?
A CPO (Contract Packaging Organization) handles the packaging and labeling of pharmaceutical products. Unlike CMOs or CDMOs, CPOs focus solely on final-stage services and do not manufacture drug substances or products.
CPOs typically provide:
- Primary and secondary packaging.
- Labeling and re-labeling.
- Serialization and traceability compliance.
- Market-specific packaging format.
Why Are CMOs, CDMOs, and CPOs Important in Pharma Manufacturing?
These organizations are vital to the pharmaceutical supply chain.
They enable drug companies to:
- Reduce capital investment in facilities and equipment.
- Access specialized expertise and technologies.
- Improve scalability and operational flexibility.
- Accelerate time to market for new therapies.
Their strategic role helps pharma firms bring safe, effective, and innovative medicines to patients more efficiently, especially in a global market with complex regulatory demands.
What Does API Stand For In Pharma?
API stands for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient, the component in a medicine that delivers the intended therapeutic effect. For example, in a cholesterol-lowering medication, Atorvastatin is the API. Drugs also contain excipients, which are inactive ingredients used to aid in the formulation, stability, or delivery of the API.